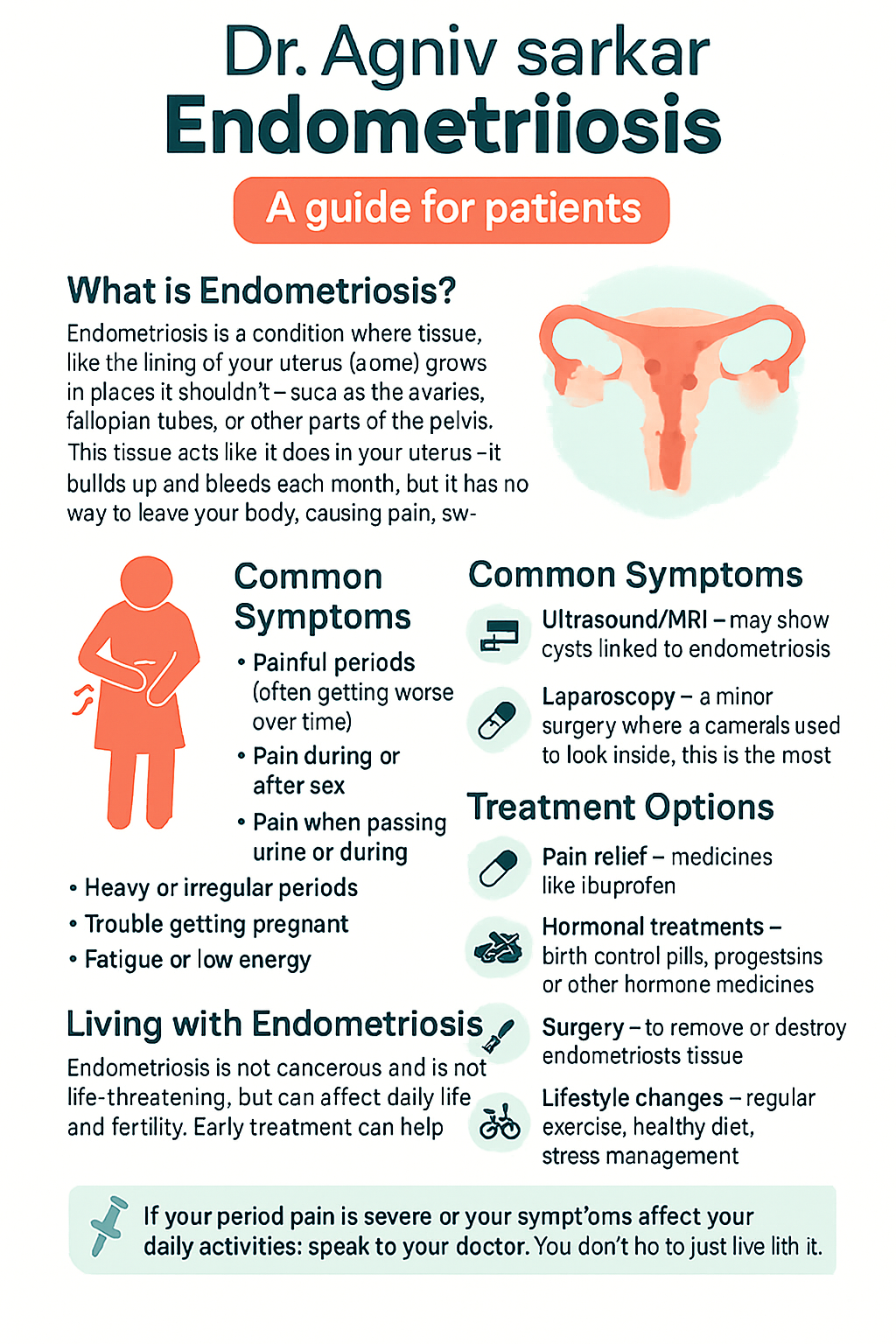
The most common symptom is pelvic pain, especially during periods. Some women may also have pain during intercourse, difficulty getting pregnant, heavy periods, or pain while passing urine or stools during menstruation. However, symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and some women may have no symptoms at all.
The exact cause is not fully known, but factors like genetics, hormonal influences, and immune system problems may play a role.
Endometriosis is not cancer and is not life-threatening, but it can affect daily life and fertility. Diagnosis usually involves an ultrasound or, in some cases, a laparoscopy (keyhole surgery).
Treatment options include pain relief medicines, hormone therapy, or surgery, depending on severity and future pregnancy plans. With timely diagnosis and management, most women can live healthy, active lives.