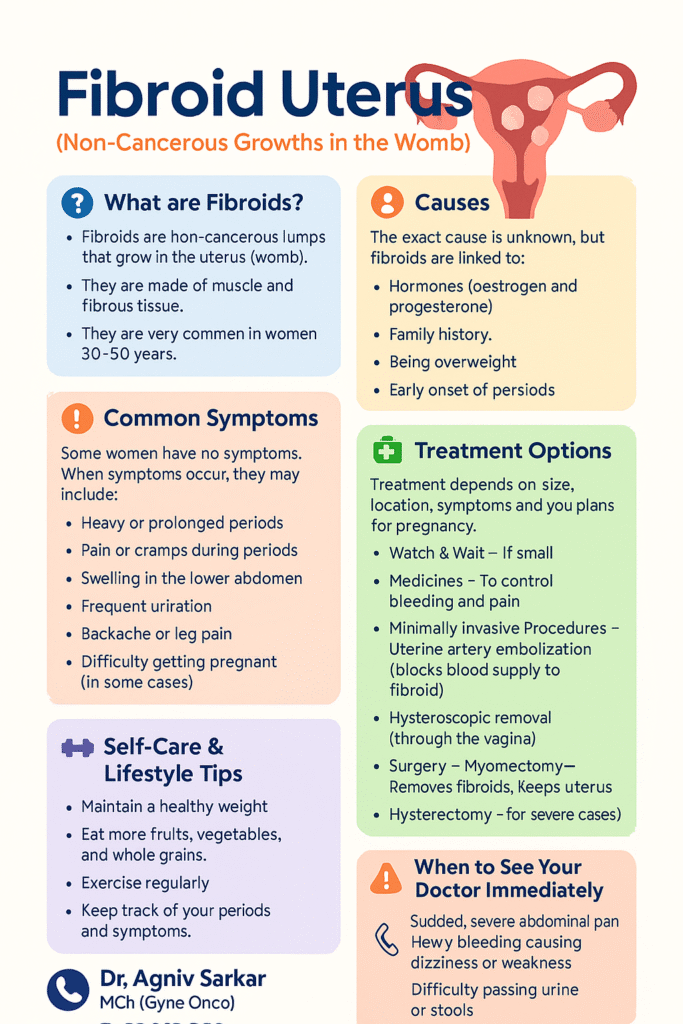
The exact cause of fibroids is not known, but they are linked to hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) and may run in families. Most fibroids do not cause problems and are found during routine check-ups. However, some women may experience symptoms like heavy or prolonged periods, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, constipation, or difficulty getting pregnant.
Diagnosis is usually made through an ultrasound. Treatment depends on the size, number of fibroids, symptoms, and whether the woman wishes to have children in the future. Options include medicines to control bleeding and pain, procedures to shrink the fibroids, or surgery to remove them.
Fibroids are not cancer and rarely turn into cancer. Many women live with fibroids without any issues. If you have symptoms affecting your daily life, it’s important to consult your doctor for the best treatment plan. Early attention can help you stay healthy and comfortable.