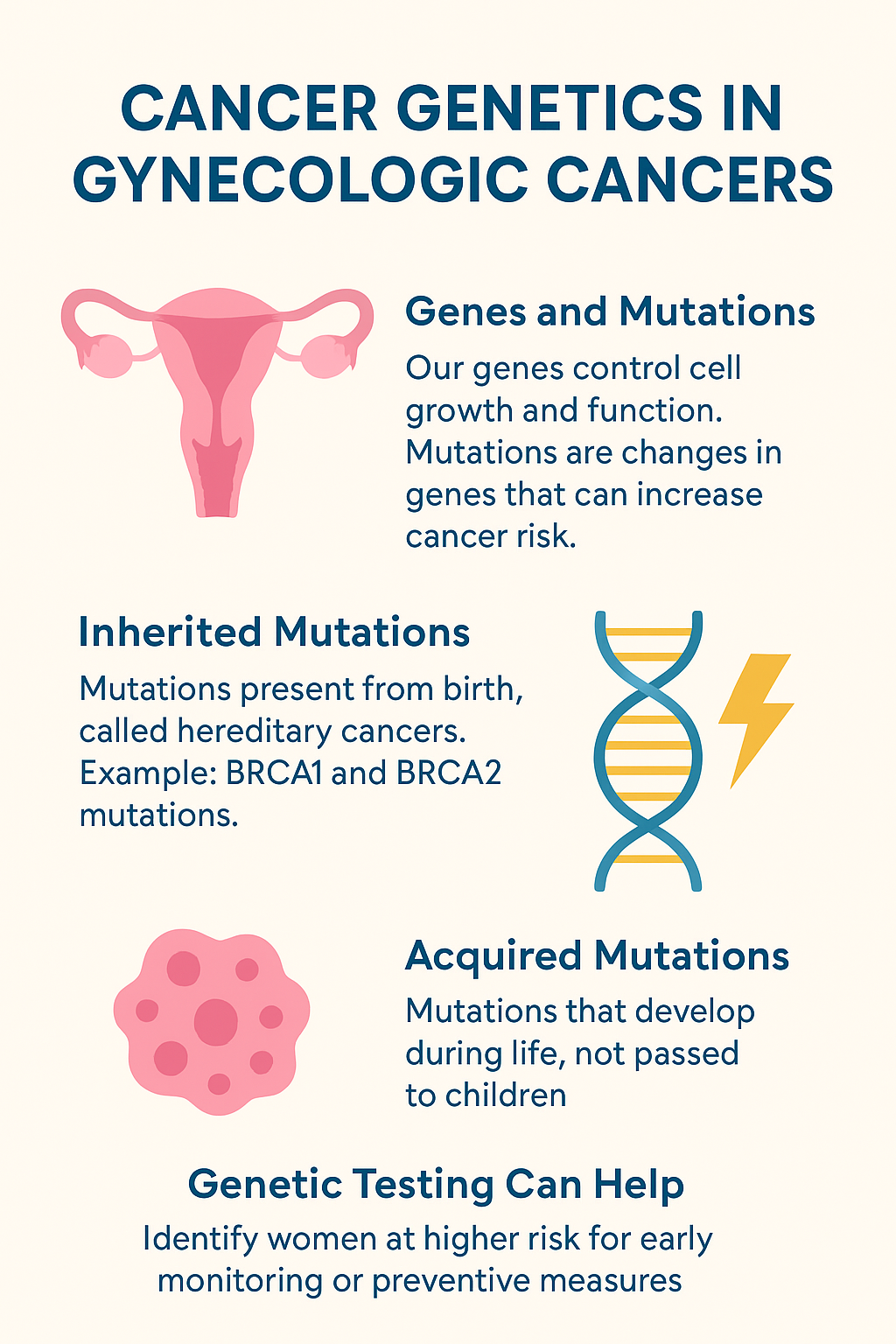
Some mutations are inherited from parents, meaning they are present from birth. These are called hereditary cancers. For example, changes in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can increase the risk of ovarian and breast cancers. Lynch syndrome, caused by mutations in specific DNA repair genes, can raise the risk of uterine and other cancers.
Other mutations develop during life, often due to aging or environmental factors, and are not passed to children. These are called acquired mutations.
Genetic testing can help identify women at higher risk, allowing for early monitoring or preventive measures. If you have a strong family history of gynecologic or breast cancer, your doctor may recommend such testing.
Understanding cancer genetics empowers women to take proactive steps for their health. Early detection, regular screenings, and informed lifestyle choices can significantly improve outcomes. Genetics is not destiny—knowledge and timely action can make a big difference.