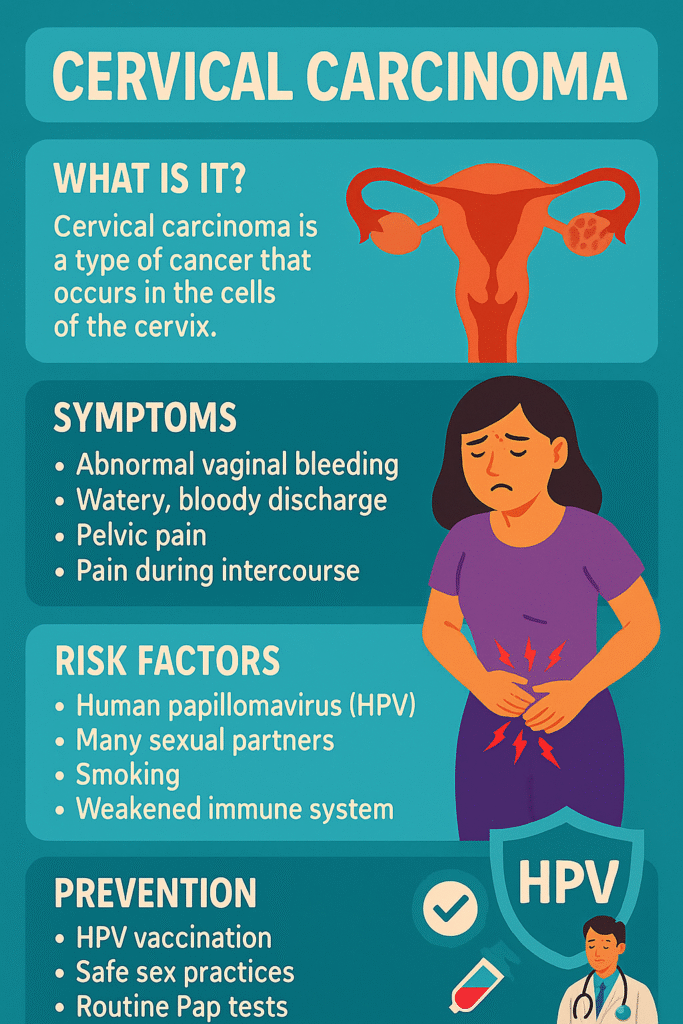
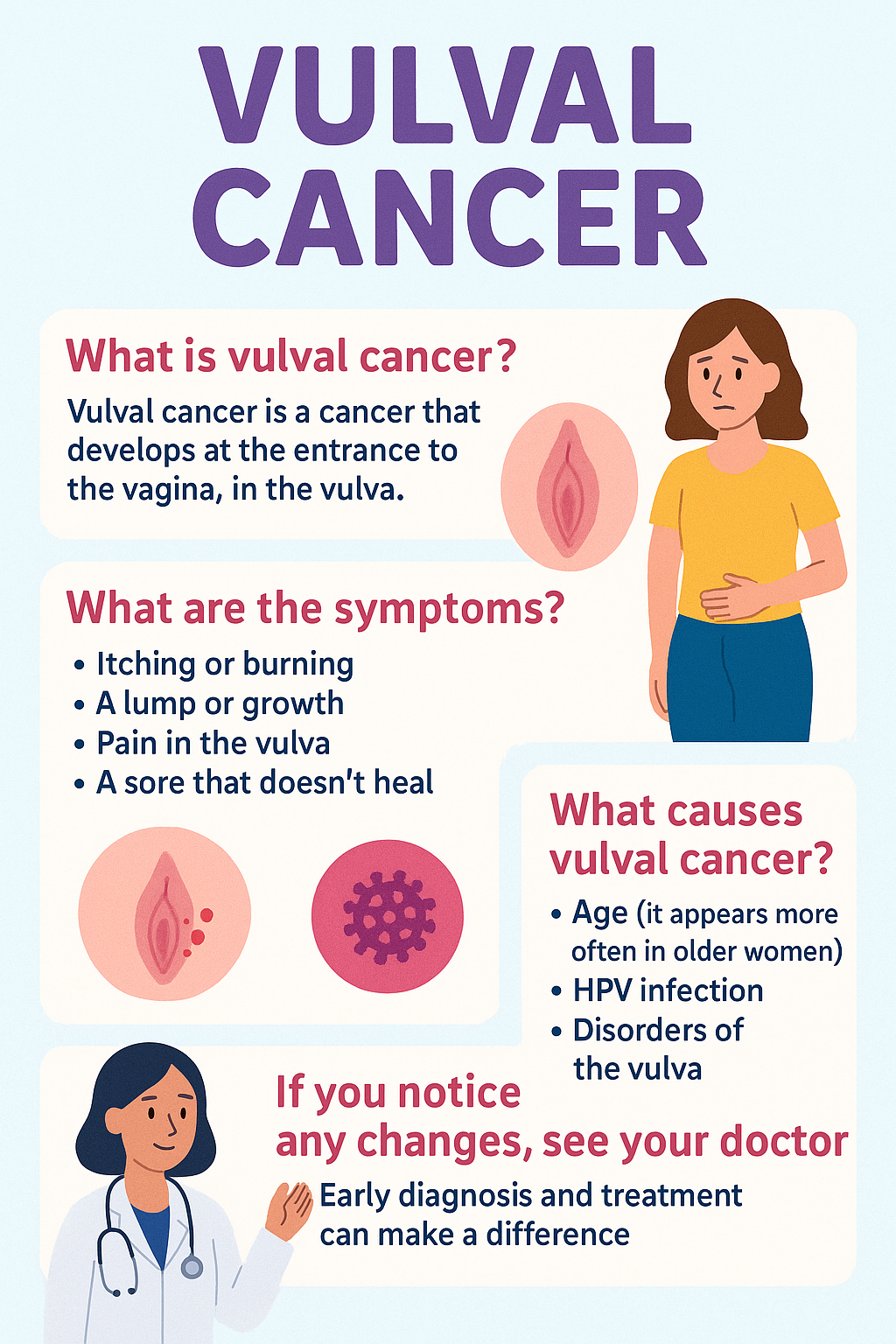
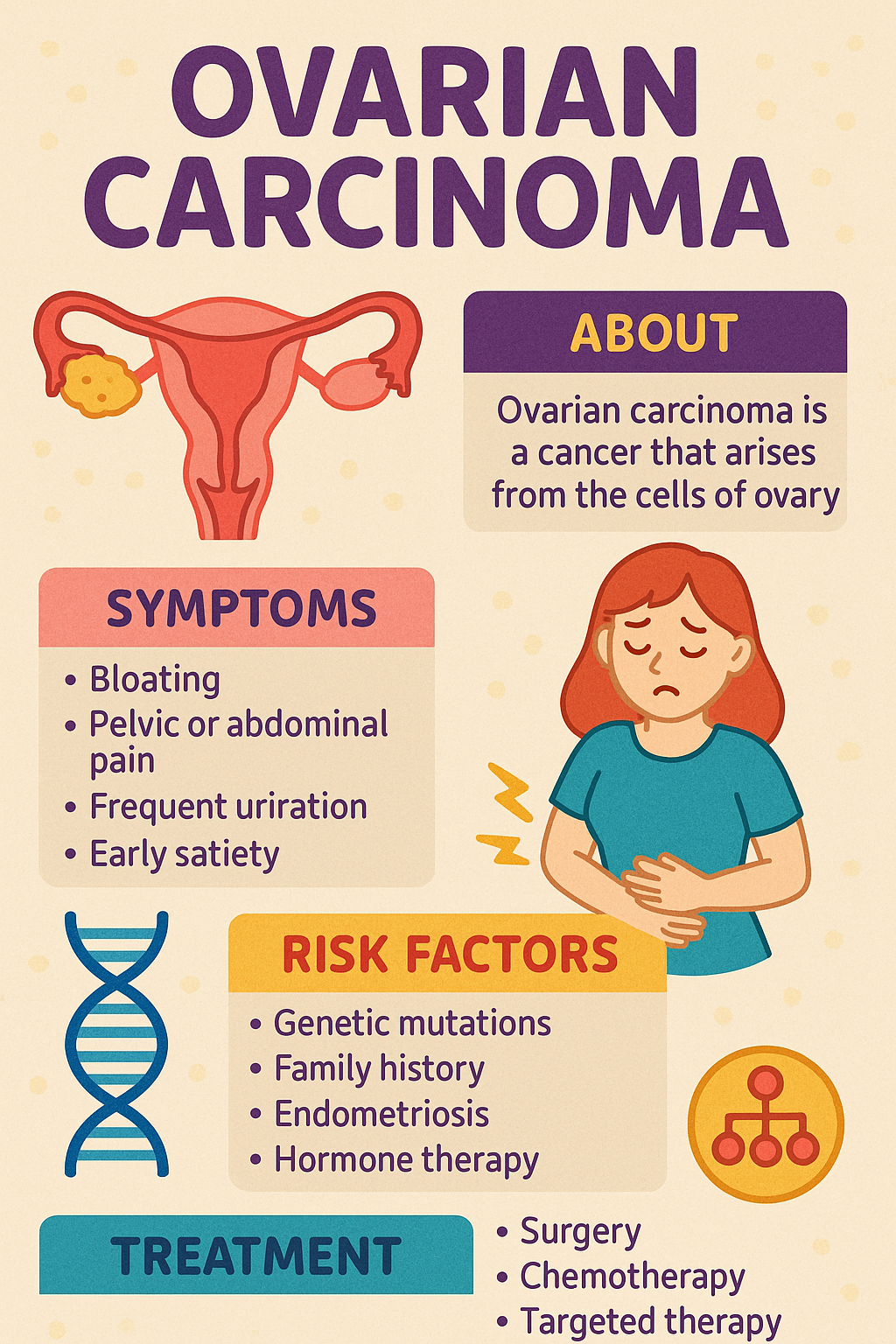
In its early stages, cervical cancer may not cause any symptoms. As it grows, symptoms can include unusual vaginal bleeding (especially after sex), foul-smelling discharge, or pelvic pain. These signs should never be ignored, and medical advice should be sought promptly.
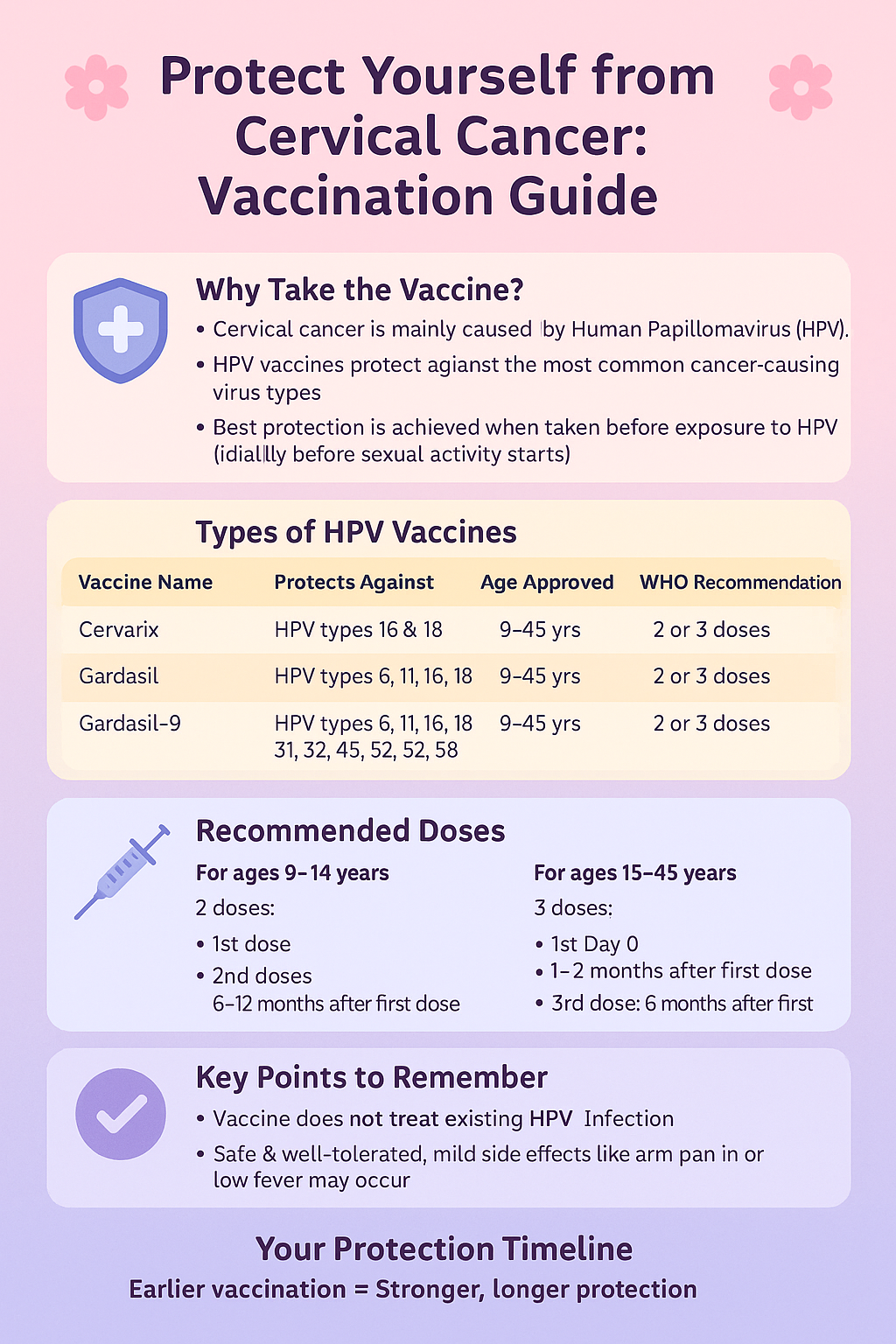
The good news is that cervical cancer is highly preventable and treatable when found early. Regular screening tests, such as the Pap smear and HPV test, can detect changes in the cervix before they turn into cancer. Vaccination against HPV, ideally given in adolescence, greatly reduces the risk.
Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination.
By attending regular screenings, getting vaccinated, and being aware of symptoms, women can greatly reduce their risk of cervical cancer and improve outcomes if it does occur. Early detection truly saves lives.