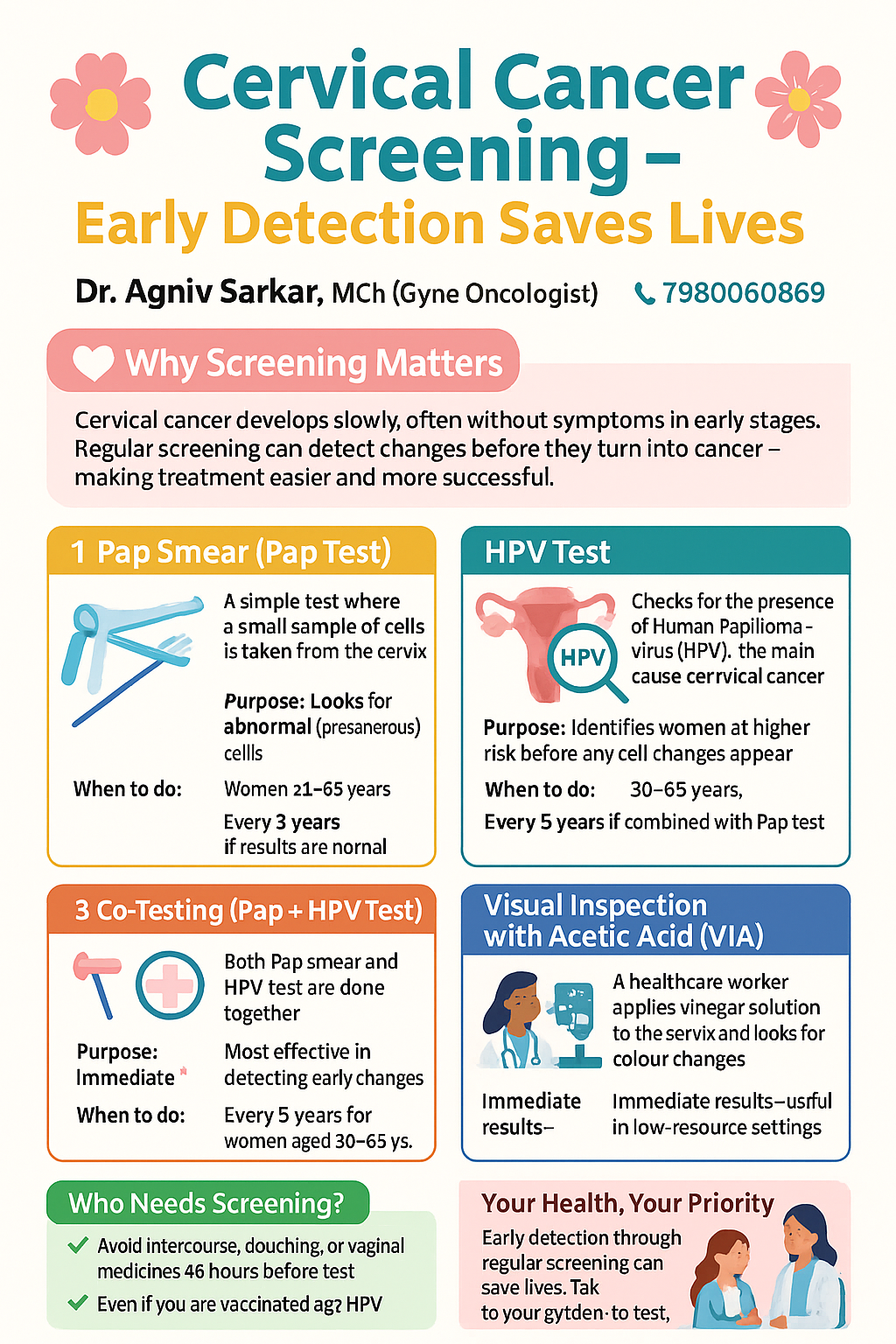
The two main screening methods are the Pap smear and the HPV (Human Papillomavirus) test. A Pap smear detects abnormal or precancerous cells on the cervix, while the HPV test checks for the virus that causes most cervical cancers. In many cases, both tests are used together for greater accuracy.
Screening is recommended for women starting at age 21. From 21 to 29 years, a Pap smear every 3 years is advised. From 30 to 65 years, either a Pap smear every 3 years, HPV testing every 5 years, or both tests together every 5 years is recommended. Women over 65 with a history of normal results may no longer need screening.
Regular screening is essential even if you feel healthy, as early-stage cervical cancer often has no symptoms. Along with vaccination against HPV, safe sexual practices, and quitting smoking, screening greatly reduces the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Timely screening empowers women to protect their health and ensures early treatment when needed.