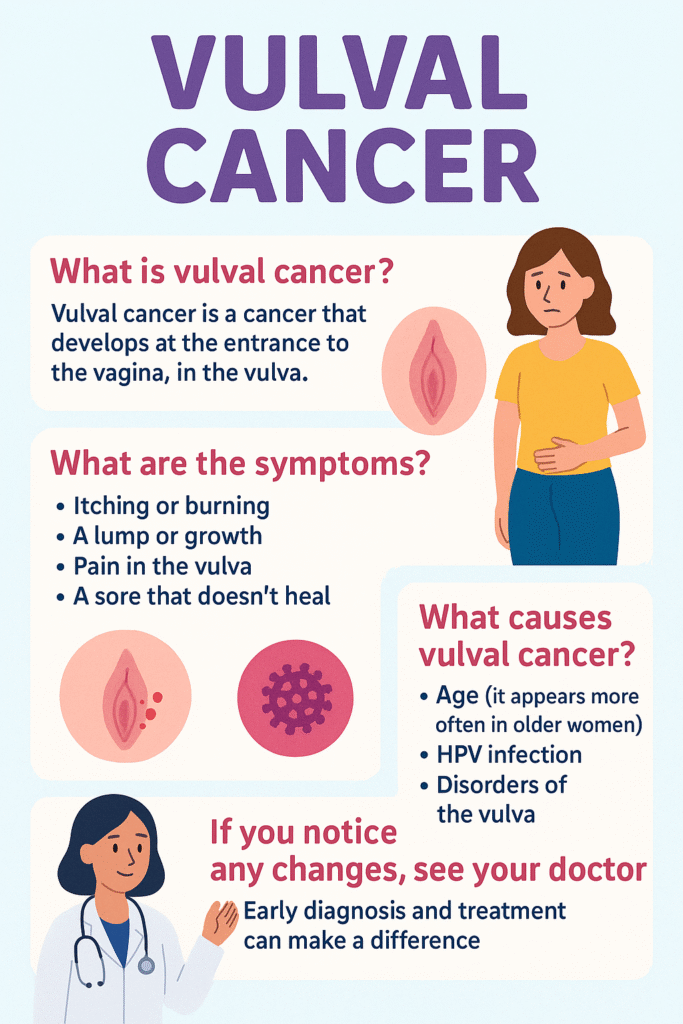
The exact cause is not always known, but certain factors increase the risk, such as long-term infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), smoking, weakened immunity, and a skin condition called lichen sclerosus.
Early signs may include persistent itching, burning, pain, swelling, changes in skin color or texture, or a lump or sore that does not heal. Some women may notice bleeding or discomfort during urination or sex.
If diagnosed early, vulval cancer is highly treatable. Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the affected tissue, and in some cases, radiotherapy or chemotherapy may be recommended.
Regular self-checks, reporting any persistent vulval changes to a doctor, and practicing safe sex to reduce HPV risk can help in prevention. HPV vaccination also offers protection against some high-risk strains.
Early detection saves lives—do not ignore symptoms or feel embarrassed to seek medical advice.