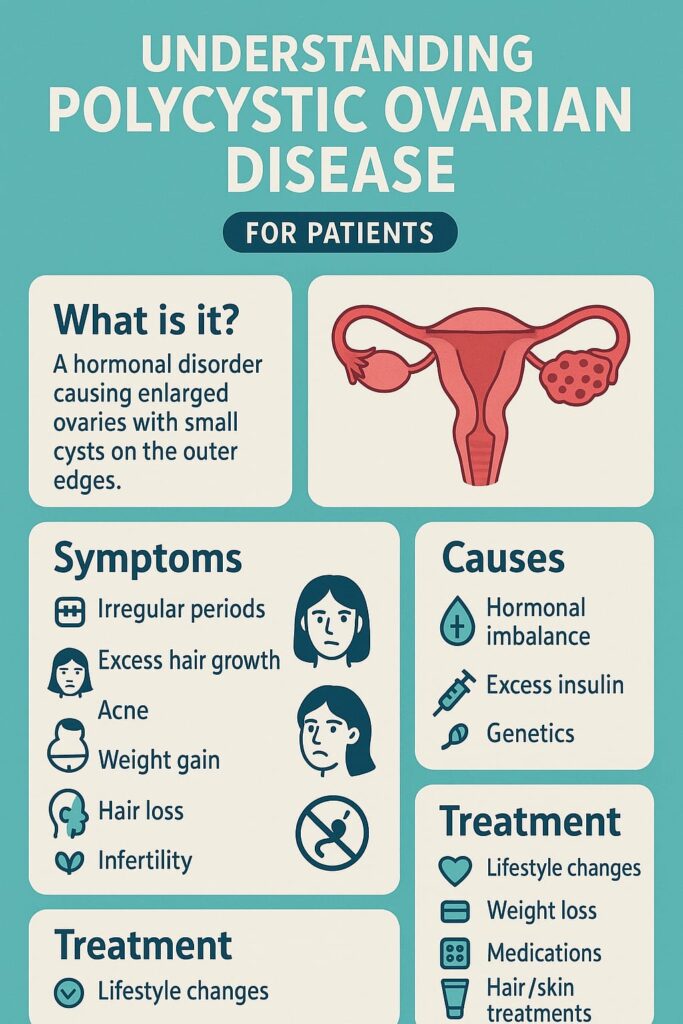
Women with PCOS may notice symptoms such as weight gain, acne, excessive facial or body hair, thinning scalp hair, and difficulty in getting pregnant. Some may also experience mood changes or fatigue. PCOS is also linked to long-term health issues like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease if not managed properly.
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully known, but genetics and lifestyle factors play a role. Diagnosis is made through a combination of symptoms, blood tests, and ultrasound.
There is no permanent cure for PCOS, but symptoms can be managed effectively. Lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can make a big difference. Doctors may also prescribe medicines to regulate periods, control symptoms, and improve fertility.
Early diagnosis and proper management can help women with PCOS lead healthy, fulfilling lives.