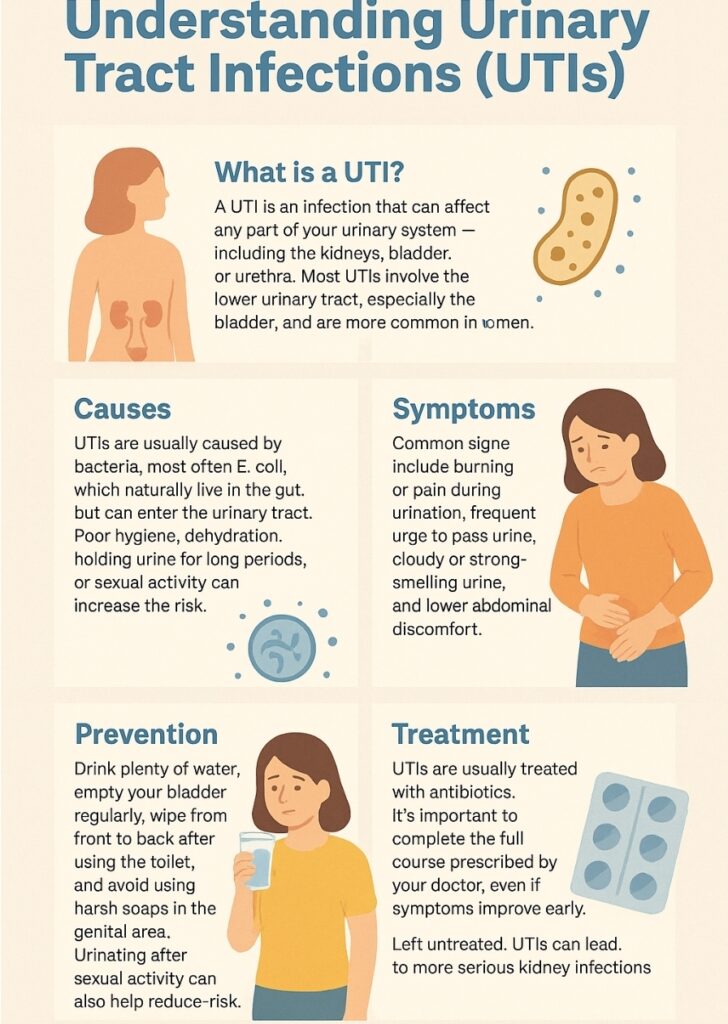
Causes: UTIs are usually caused by bacteria, most often E. coli, which naturally live in the gut but can enter the urinary tract. Poor hygiene, dehydration, holding urine for long periods, or sexual activity can increase the risk.
Symptoms: Common signs include burning or pain during urination, frequent urge to pass urine, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and lower abdominal discomfort. If the infection spreads to the kidneys, symptoms may include fever, back pain, and nausea — which require urgent medical attention.
Prevention: Drink plenty of water, empty your bladder regularly, wipe from front to back after using the toilet, and avoid using harsh soaps in the genital area. Urinating after sexual activity can also help reduce risk.
Treatment: UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics. It’s important to complete the full course prescribed by your doctor, even if symptoms improve early. Left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious kidney infections.
With prompt care and healthy habits, UTIs can be managed and prevented effectively.